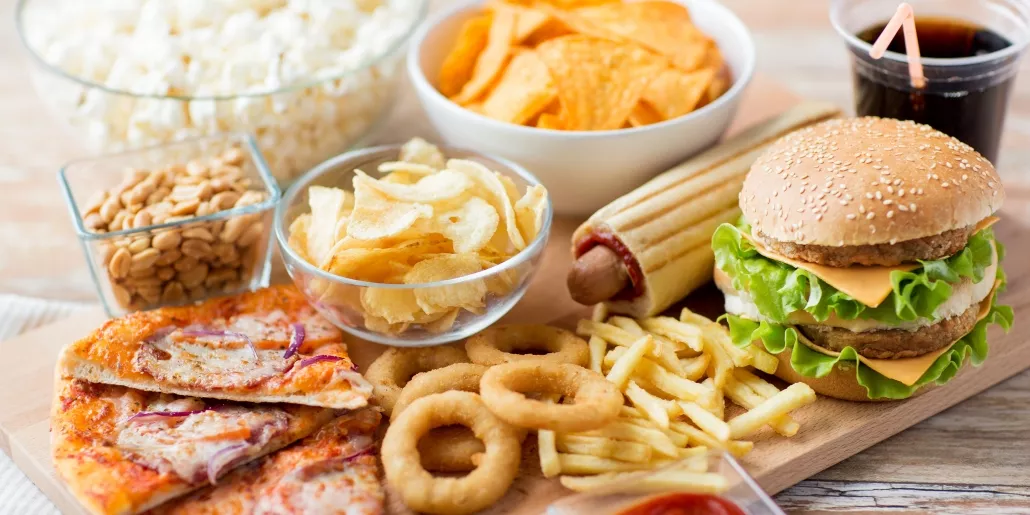
Through the course of the last several decades, the rate of obesity has progressively increased and is now one of the leading causes of death worldwide. The World Health Organization reports 1.9 billion adults were overweight in 2016 and 650 million were considered obese. According to the Center for Disease Control, the prevalence of obesity in the United States was 30.5% in 1999. This increased to 42.4% by 2017. In conjunction with this, chronic illnesses associated with obesity such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease are now among the top causes of death in the United States. Several factors have been attributed to this epidemic with the western diet considered to be a major contributor to the growing rate of obesity in the United States. Although current lifestyle trends emphasize the importance of eating healthy, we continue to see foods high in fat and sugar as major components of the Western diet which has corresponded to the steady rise in obesity.
what should be eaten
The recommended daily caloric intake depends on an individual’s age, gender, and level of physical activity. Weight gain occurs when more calories are consumed than expended. Healthy weight loss can be achieved with a daily caloric intake of 1,200–1,500 for women and 1,500–1,800 for men. The U.S. Departments of Health and Human Services (DHHS) and Agriculture (USDA) have released the Dietary Guidelines for 2015 to 2020. This plan encourages a diet rich in nutrients while limiting calories from added sugars, saturated and trans fats, and sodium. Added sugars and saturated fats should each contribute less than 10% of the daily caloric intake. The American Heart Association recommends that women consume less than 6 teaspoons of sugar daily and men consume less than 9 teaspoons of sugar daily. Finally, the recommended daily sodium intake should be less than 2,300 mg.
A healthy diet should include foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy. Eating a healthy diet not only results in weight loss, it can decrease the risk of cardiovascular disease.
What is eaten
The typical Western diet is low in fruits and vegetables, and high in fat and sodium. Moreover, this diet consists of large portions, high calories, and excess sugar. This excess sugar accounts for more than 13% of the daily caloric intake with beverages constituting 47% of these added sugars. Other sources include cookies, cakes, and candy.
Although fruits and vegetables contain natural sugars, they provide nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants while added sugars only contribute calories. The western diet is also noted to be high in saturated and trans fats. These fats not only contribute more calories; they increase low-density lipoproteins leading to atherosclerosis.
There has recently been increasing interest in the effect of dietary patterns on the immune system. One study compared mice that were fed a western diet to mice that were fed a standard fiber-rich diet. The western diet consisted of foods high in fats and sugars and low in fiber. These mice were found to have higher levels of inflammation and sepsis resulting in worse outcomes.
Individuals who are obese or overweight are at a higher risk of developing chronic illnesses such as type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, sleep apnea, or cancer. In fact, half of all Americans have a preventable chronic illness. According to the American Heart Association, 81 million American adults have cardiovascular disease which includes coronary artery disease or cerebrovascular disease. One-third of American adults have hypertension and more than 85% of patients with type 2 diabetes are considered overweight.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, once a disease primarily seen in adults, now presents in younger generations as a result of increasing childhood and adolescent obesity. According to the CDC, 13.7 million children and adolescents are considered obese in the United States.
Multiple studies have also shown that obesity during midlife increases the risk of developing dementia. With fifty million people affected by dementia worldwide, there has been great interest in identifying preventable risk factors. A recent study evaluated the effect of diet modification and weight loss in elderly obese patients with mild cognitive impairment. These patients reduced their caloric intake and consumed more fruits, vegetables, fibers, and whole grains. The findings proved that weight reduction through diet modification improves cognition with these individuals showing improvements in verbal memory, verbal fluency, executive function and global cognition.
Studies from several countries have shown that diets consisting of fruits, vegetables, seafood, chicken, and whole grains are associated with better semen quality while consumption of high amounts of trans and saturated fats were linked to poor semen quality.
Karimi, H.
Master of clinical Nutrition & Dietetics
Reference
- Rakhra V, et al. Obesity and the Western Diet: How We Got Here. Mo Med.2020.