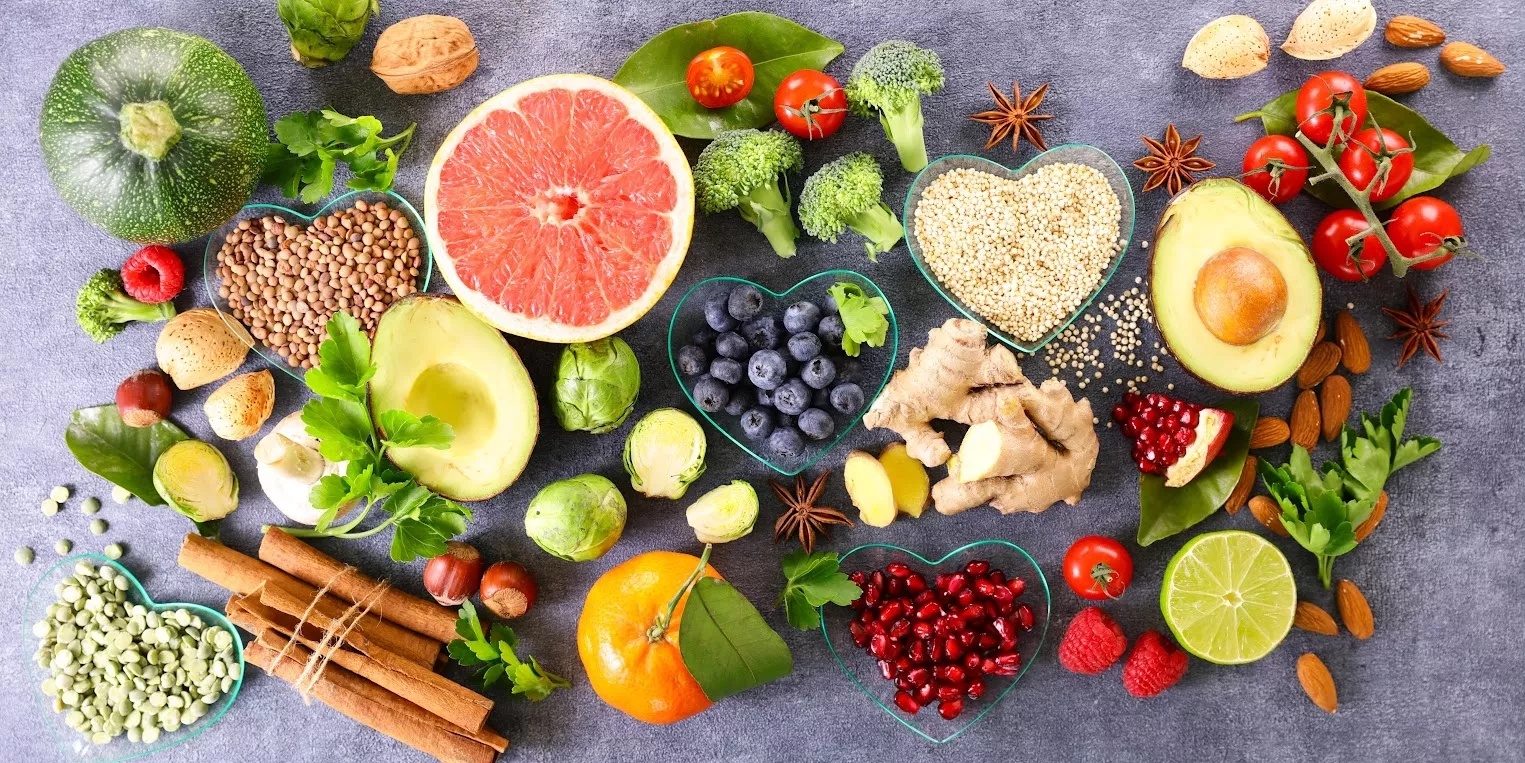
The main world health problems are obesity and chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular problems. They are etiologically linked with the reduced consumption of fruits and vegetables and increased intake of salt, fats from animal origins, trans fatty acids, sugars, and sugary beverages.
Plants synthesize various phenolic compounds that are present in different parts of the plant, but particularly in fruits, leaves, and seeds. Many foods (plant-based) in a healthy diet like fruits and vegetables contain most of the naturally occurring polyphenols. These are not merely a source of non-nutritive compounds containing phenolics but a great source of a large variety of nutritional compounds containing minerals (iron, copper, zinc, manganese, and selenium), vitamins (C, A, E), and dietary fibers. These minerals and vitamins serve as antioxidants that help in reducing several chronic and age-related diseases, mainly diabetes, cancer, coronary heart disease, CVD, and provide beneficial health benefits and encourage healthy aging. Antioxidants also help in reducing inflammation.
Bioactive Compounds
Bioactive compounds are important complexes, found in foods and are efficient in regulating different metabolic activities and results in better health. Furthermore, several fruits constitute a broad diversity and large content of bioactive compounds particularly tannins, stilbenes, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. Polyphenols play a vital part in fruits and are used as antioxidants and colorants. Intake of dietary antioxidants helps to uphold an adequate antioxidant status in the human body. A substantial amount of research on polyphenols is emphasized on their antioxidant properties after they are believed to have optimistic effects on age-related chronic pathologies. Various studies have also reported that polyphenols rich diet can prevent oxidative damage leading to aging.
Presence of antioxidants, aid in delaying or preventing oxidative damage of biomolecules by ROS which contain reactive free radicals including hydroxyl, peroxyl, alkoxyl, superoxide, and non-radicals such as hypochlorous, hydrogen peroxide, etc. The anthocyanins in fruits are also the most studied phenolic with a large variety of bioactivities including anti-aging, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Antioxidants scavenge these radicals by counteracting the formation of free radicals by attaching to metal ions or suppressing the initiation and chain-breaking propagation, by quenching superoxide and singlet oxygen, and by reducing hydrogen peroxide and thus circumventing several age-linked diseases like type 2 diabetes, inflammation, cancer, and CVD.
Several vivid fruits and vegetables are extensively tested for their potential to neutralize free radicals that can destroy DNA and cell membranes via a mechanism called oxidative stress, which is responsible for most aging-related malfunctions and disorders. While several fruits like blueberries, grapes, cranberries themselves are not a remedy for all of them, they contain a variety of substances such as vitamins, fibers, and antioxidants that have health benefits. Antioxidants in fruits and vegetables appear to have the most credible role in delaying or preventing aging, heart disease, cancer, and other age-related disorders.
Inflammation is a physiological process of the body’s response to various kinds of injuries, but the deregulation of the inflammatory systems can cause severe damage to the cells and tissues of the host and contribute to disease development. Chronic inflammation is associated with multiple diseases, which include Alzheimer’s disease, CVD, metabolic syndrome, cancer, type 2 diabetes, and atherosclerosis. Significant studies indicate that the intake of a fruit-rich diet is related to a reduced risk of inflammation-associated diseases. In-vitro and in-vivo research have highlighted the potential beneficial effects of fruits on chronic inflammatory diseases. Cai et al. in his research stated that supplementation of cranberry decreases the colonic levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice treated with dextran sodium sulfate. Phytochemicals in raspberry effectively modulate gene expression, enzyme activity, and cellular pathways. In addition, to reduce the production of oxidized-LDL through their antioxidant activity, raspberry phytochemicals have shown anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic properties that protect against CVD. The systematic consumption of polyphenol-rich foods, strawberry, or antioxidant has been shown to prevent inflammatory and fibrinolytic factors in foods.
Fruits and vegetables are rich and valuable sources of bioactive compounds for improving health and reducing the risks of noncommunicable chronic diseases.
Karimi, H
Master of clinical Nutrition & Dietetics
Reference
1-Strategies to achieve a healthy and balanced diet: fruits and vegetables as a natural source of bioactive compounds. Agri-Food Industry Strategies for Healthy Diets and Sustainability New Challenges in Nutrition and Public Health.2020. Pages 51-88.
2-Dhalaria R, et al. Bioactive Compounds of Edible Fruits with Their Anti-Aging Properties: A Comprehensive Review to Prolong Human Life. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Nov; 9(11): 1123.